Motivation
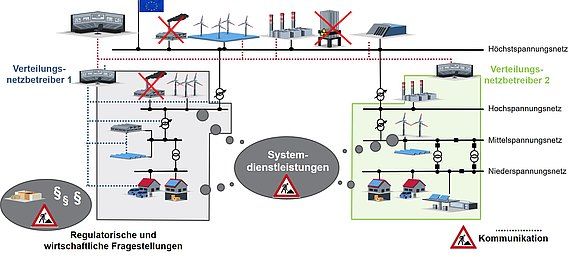
Die bisherigen Systemdienstleistungen (SDL) für einen sicheren Betrieb der Stromnetze wurden seit Jahrzehnten vorwiegend von den Synchrongeneratoren der konventionellen Großkraftwerke bereitgestellt. Die Systemdienstleistungen umfassen die Frequenzhaltung, Spannungshaltung, Betriebsführung und den Versorgungswiederaufbau. Zukünftig müssen diese Systemdienstleistungen durch eine Vielzahl dezentraler Erzeuger auf Basis erneuerbarer Energien und Lasten in den Verteilungsnetzen im Sinne einer sektorenübergreifenden Energiewende erbracht werden. Hierdurch steigen die Anforderungen an die Netzbetriebsführung und das spannungsebenenübergreifende Management von Systemdienstleistungen. Dies führt ebenfalls zu steigenden Anforderungen an den Umfang und die Resilienz der digitalen Transformation des Energiesystems sowie zu neuen Anforderungen an die wirtschaftlichen und rechtlichen Rahmenbedingungen des zukünftigen elektrischen Energieversorgungssystems.
Abbildung 1: Zukünftige Herausforderungen bei der Bereitstellung von Systemdienstleistungen. © elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme der TU Braunschweig
Ziele des Projektes
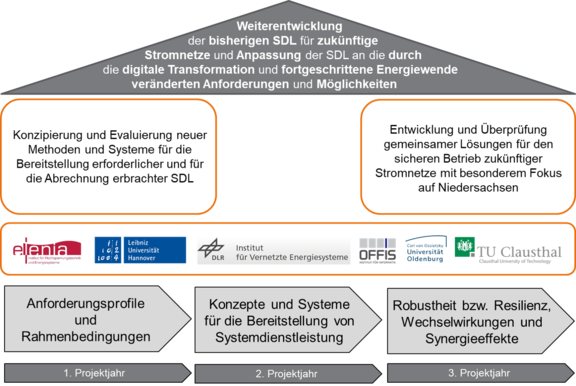
Das EFZN-Leitprojekt „SiNED – Systemdienstleistungen für sichere Stromnetze in Zeiten fortschreitender Energiewende und digitaler Transformation“ hat zum Ziel, die bisherigen Systemdienstleistungen für zukünftige Stromnetze weiterzuentwickeln und an die durch die Digitalisierung und fortgeschrittene Energiewende veränderten Anforderungen und Möglichkeiten anzupassen.
Es werden Lösungen für den sicheren Betrieb der zukünftigen Stromnetze – unter Berücksichtigung der besonderen Situation in Niedersachsen – entwickelt und untersucht. Gerade für die windstarken Regionen Niedersachsens ist es von besonderer Bedeutung, verbesserte Lösungen für Systemdienstleistungen zur Bewältigung fluktuierender Einspeisung und für das Engpassmanagement durch Stromspeicherung und zuschaltbare Lasten zu finden.
Abbildung 2: Übergeordnetes Projektziel und Teilziele. © EFZN
Zur Beantwortung der zentralen gemeinsamen Forschungsfrage von SiNED werden zusammenfassend folgende Leifragen für das Verbundprojekt definiert:
1. Wie kann zukünftig der veränderte Bedarf an Systemdienstleitungen, die zunehmend durch EE-Anlagen erbracht werden müssen, bis 2050 gedeckt werden?
2. Wie kann der Bedarf an Systemdienstleistungen durch die Flexibilitätsbereitstellung dezentraler Netznutzer gedeckt werden und wie kann diese Herausforderung von umrichterdominierten Verteilungsnetzen gelöst werden?
3. Wie kann die Flexibilität für die Bereitstellung von Systemdienstleistungen in Verteilnetzen unter Berücksichtigung der Resilienz informationstechnisch erschlossen werden?
4. Welche wirtschaftlichen Optimierungspotentiale sind bei der Bereitstellung von Systemdienstleistungen möglich, welche (datenschutz-)rechtlichen Restriktionen sind zu beachten und welche Anpassungen des Ordnungsrahmens sind erforderlich?
Aufbau des Projektes
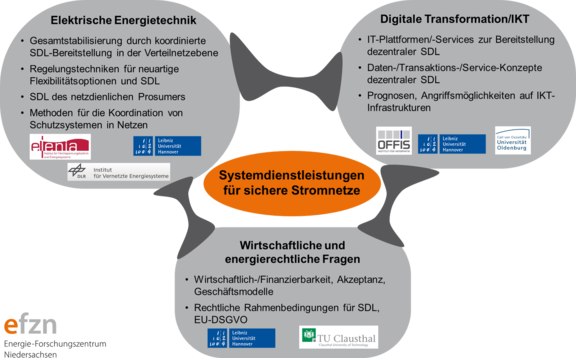
Das Verbundvorhaben gliedert sich in insgesamt neun integrierte, verzahnte Teilprojekte (TP), die in drei Kompetenzbereiche gegliedert sind.
Abbildung 3: Aufbau des Projektes. © EFZN
Daten zum Projekt
Sprecher
Professor Dr.-Ing. Bernd Engel
TU Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme
Projektkoordinator
Cornelius Biedermann
TU Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme
Telefon: 0531 391 7788
E-Mail: cornelius.biedermanntu-braunschweigde
Projektpartner
TU Braunschweig – elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme
Professor Dr.-Ing. Bernd Engel und
Professor Dr.-Ing. Michael Kurrat
Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt – Institut für Vernetzte Energiesysteme Oldenburg
Professor Dr. Carsten Agert
OFFIS e.V. – Institut für Informatik Oldenburg
Professor Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff
Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg – Department für Informatik, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme
Professorin Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße
Leibniz Universität Hannover – Institut für Elektrische Energiesysteme, Fachgebiet Elektrische Energieversorgung
Professor Dr.-Ing. habil. Lutz Hofmann
Leibniz Universität Hannover – Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik
Professor Dr. Michael H. Breitner
TU Clausthal – Institut für deutsches und internationales Berg- und Energierecht
Professor Dr. jur. Hartmut Weyer
Laufzeit
01.11.2019 - 31.10.2024
Fördernde Stelle
Niedersächsisches Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kultur – Zusätzliche Förderung von Wissenschaft und Technik in Forschung und Lehre aus Mitteln des Niedersächsischen Vorab
Kompetenzbereich „Elektrische Energietechnik“
TP 1.1: Gesamtstabilisierung durch koordinierte Systemdienstleistungen-Bereitstellung in der Verteilnetzebene
Verantwortlicher Mitarbeiter: Neelotpal Majumdar, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Elektrische Energiesysteme, Fachgebiet für Elektrische Energieversorgung - Mehr erfahren >
TP 1.2: Regelungstechniken für neuartige Flexibilitätsoptionen und Systemdienstleistungen
Verantwortliche Mitarbeiterin: Julian Beyrodt, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt - Institut für Vernetzte Energiesysteme Oldenburg (DLR-VE) - Mehr erfahren >
TP 1.3: Systemdienstleistungen des netzdienlichen Prosumers
Verantwortlicher Mitarbeiter: Carsten Wegkamp, TU Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme - Mehr erfahren >
TP 1.4: Methoden für die Konfiguration und Koordination von Schutzsystemen in Netzen
Verantwortlicher Mitarbeiter: Marc René Lotz, TU Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme / Ostfalia Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften - Mehr erfahren >
Kompetenzbereich „Digitale Transformation / Informations- und Kommunikationstechnologie (IKT)“
TP 2.1: IT-Plattformen/-Services zur Bereitstellung dezentraler Systemdienstleistungen
Verantwortlicher Mitarbeiter: Michael Brand, OFFIS e.V. - Institut für Informatik Oldenburg - Mehr erfahren >
TP 2.2: Daten-/Transaktions-/Service-Konzepte dezentraler Systemdienstleistungen
Verantwortlicher Mitarbeiter: Jens Sager, Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg - Department für Informatik, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme - Mehr erfahren >
TP 2.3: Prognosen, Angriffsmöglichkeiten auf IKT-Infrastrukturen
Verantwortliche Mitarbeiterin: Sarah Lier, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik - Mehr erfahren >
Kompetenzbereich „Wirtschaftliche und energierechtliche Fragen“
TP 3.1: Wirtschaftlich-/Finanzierbarkeit, Akzeptanz, Geschäftsmodell
Verantwortliche Mitarbeiterin: Sarah Lier, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik - Mehr erfahren >
TP 3.2: Rechtliche Rahmenbedingungen für Systemdienstleistungen, EU-DSGVO
Verantwortlicher Mitarbeiter: Jan Schlüpmann, TU Clausthal, Institut für deutsches und internationales Berg- und Energierecht - Mehr erfahren >
Veröffentlichungen
Gerlach, J., Beutel, V., Wegkamp, C., Breitner, M. H., Greißendörfer, S., Engel, B., von Maydell, K. (2024): Navigating the energy transition: Identifying critical success factors for ancillary services provision and sustainable energy solutions in Germany, Heliyon, Jg. (2024). E-ISSN: 2405-8440. Online verfügbar unter: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27643
Lier, S. K., Gerlach, J., Breitner, M. H. (2024): What is Ethical AI? - Design Guidelines and Principles in the Light of Different Regions, Countries, and Cultures, Hawaii International Conference on System Science, Honolulu, Hawaii, 2024.
Majumdar, N., Kengkat, P., Yermekbayev, R., Hofmann, L. (2023): Reliability parameterised distribution grid flexibility aggregation considering renewable uncertainties, Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Dublin, Ireland, 2023.
Majumdar, N., Sarstedt, M., Hofmann, L. (2023): Distribution Grid Power Flexibility Aggregation at Multiple Interconnections between the High and Extra High Voltage Grid Levels,IEEE PES GTD International Conference and Exposition (GTD), Istanbul, Turkiye, 2023, pp. 303-309. Online verfügbar unter: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2303.01107
Wagner, H., Lüdecke, M., Scheunert, A., Wegkamp, C., Engel, B., Weyer, H. (2023): Technical and Legal Analysis of the Grid-Serving Multi-Use of Battery Storage Systems for Prosumers, 22nd Wind & Solar Integration Workshop, Copenhagen, Denmark, 26–28 September 2023.
Wegkamp, C., Ferk, M., Grobler, J., Engel, B. (2023): Application of Residential Prosumer Flexibility for Frequency Control – Analysis and Simulative Investigation Considering Control Power and Inertia, 22nd Wind & Solar Integration Workshop, Copenhagen, Denmark, 26–28 September 2023.
Lier, S. K., Gerlach, J., Breitner, M. H. (2023): Who Needs XAI in the Energy Sector? A Framework to Establish Black Box Explainability, International Conference on Information Systems, Hyderabad, India (Accepted for publication), 2023.
Gerlach, J., Lier, S. K., Hoppe, P., Breitner, M. H. (2023): Critical Success Factors for AI-driven Smart Energy Services, Americas Conference on Information Systems, Panama City, Panama, 2023.
Bokker, O., Schlachter, H., Beutel, V., Geißendörfer, S., von Maydell, K. (2023): Reactive Power Control of a Converter in a Hardware-Based Environment Using Deep Reinforcement Learning, Energies. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI), 2023.
Wegkamp, C., Hadlak, M., Wagner, H., Kohlhepp, J., Engel, B. (2023): Optimized provision of local ancillary services with sensitivity factors using prosumer flexibility, CIRED 2023 International Conference & Exhibition on Electricity Distribution, Rome, 2023.
Biedermann, C., Beutel, V., Beyrodt, J., Brand, M., Buchholz, S., Gerlach, J., Majumdar, N., Leveringhaus, T., Lotz, M. R., Raeiszadeh, A., Scheunert, A., Baboli, P. T., Tiemann, P. H., Wegkamp, C., Agert, C., Breitner, M. H., Engel, B., Geissendörfer, S., Hofmann, L., Könemund, M., Kurrat, M., Lehnhoff, S., von Maydell, K., Nieße, A., Weyer, H., (2023): Research Project SiNED Insights – Ancillary Services for Reliable Power Grids in Times of the Progressive German Energiewende and Digital Transformation, ETG Congress 2023 25.05.2023 - 26.05.2023 Kassel, Germany.
Gerlach, J., Meyer, L., Werth, O., Breitner, M. H. (2023): Vermarktungsmöglichkeiten und Entwicklungsroadmap für Biogasanlagen, DBFZ.
Baboli, P. T., Raeiszadeh, A., Brand, M., Lehnhoff, S. (2023): Demo Abstract: IT Platform for Provision of Ancillary Services from Distributed Energy Resources, DACH+ Conference on Energy Informatics, Vienna, Austria, 2023.
Lotz, M. R., Koenemund, M., Kurrat, M. (2023): Adaption of Inverter-Based System Controls to Reduce the Negative Impact of Intermediate Infeed on Distance Protection Systems, ETG Congress 2023, Kassel, Germany, 2023.
Gerlach, J., Hoppe, P., Jagels, S., Licker, L., Breitner, M. H. (2022): Decision Support for Efficient XAI Services - A Morphological Analysis, Business Model Archetypes, and a Decision Tree, Electronic Markets, 2022.
Wegkamp, C., Skruk, B., Engel, B. (2022): Analysis and Systematic Comparison of Concepts for Voltage Control with Inverted-Based Prosumer Devices, 21st Wind & Solar Integration Workshop, The Hague, Netherlands, 12.-14. Oktober 2022.
Teimourzadeh Baboli, P., Raeiszadeh, A., Brand, M., Lehnhoff, S. (2022): Reliability-Sensitive Optimization for Provision of Ancillary Services by Tempo-Spatial Correlated Distributed Energy Resources, in17th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications (SOCO2022), Salamanca, Spain.
Teimourzadeh Baboli, P., Raeiszadeh, A., Brand, M., Lehnhoff, S. (2022): Multivariate Cross-Correlated Reliability Modeling of Wind Turbines using Pair-Copula Functions, in the IEEE ISGT Europe, Serbia.
Wegkamp, C., Buchholz, S., Tiemann, P.H., Engel, B., Weyer, H., Nieße, A. (2022): Specific Product Characteristics of System Services and a Discussion of the Joint Market-Based Pro-curement in a Single Product, International Ruhr Energy Conference, 27.-28. September 2022.
Klabunde, F., Wegkamp, C., Engel, B. (2022): Provision of grid-serving flexibility by agricultural operations and households in rural power distribution grids, NEIS 2022 - Conference on Sustainable Energy Supply and Energy Storage Systems, 26.-27. September 2022.
Gerlach, J., Werth, O., Breitner, M.H. (2022): Artificial Intelligence for Cyberse-curity: Towards Taxonomy-based Archetypes and Decision Support,In Proceedings of the Forty-Third International Conference on Information Systems, Copenhagen 2022.
Gerlach, J., Scheunert, A., Breitner, M.H. (2022): PERSONAL DATA PROTECTION RULES! GUIDELINES FOR PRIVACY-FRIENDLY SMART ENERGY SERVICES, In Pro-ceedings of the Thirtieth European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2022), Timisoara, Romania. Online verfügbar unter: https://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2022_rp/123
Privacy-friendly processing of personal data is proving to be increasingly challenging in today’s energy systems as the amount of data grows. Smart energy services provide value creation and co-creation by processing sensible user data collected from smart meters, smart home devices, storage systems, and renewable energy plants. To address this challenge, we analyze key topics and develop design requirements and design principles for privacy-friendly personal data processing in smart energy services. We identify these key topics through expert interviews, text-mining, and topic modelling techniques based on 149 publications. Following this, we derive our design requirements and principles and evaluate these with experts and an applicability check with three real-world smart energy services. Based on our results and findings, we establish a further research agenda consisting of five specific research directions.
Majumdar, N., Sarstedt, M., Kluß, L., Hofmann, L. (2022): Linear Optimization Based Distribution Grid Flexibility Aggregation Augmented With OLTC Operational Flexibilities, IEEE Access, 10, 77510-77521.
Tiemann, P.H., Nebel-Wenner, M., Holly, S., Frost, E., Jimenez Martinez, A., Nieße, A. (2022): Operational flexibility for multi-purpose usage of pooled battery storage systems, Energy Informatics 5(1), 14–26. Online verfügbar unter: DOI: 10.1186/s42162-022-00209-4
The multi-purpose usage of battery energy storage systems (BESSs) increases the exploitation of their flexibility potential. This can be further enhanced when a large number of small BESSs are combined into a swarm and marketed collectively by an aggregator. To this end, a unified representation of remaining flexibility for each BESS is needed that meets the requirements of both, a multi-purpose usage and a distributed swarm design. In this work, we present a compact model which we call abstract multi-purpose-limited flexibility (Amplify). It can be used by an aggregator to determine how much flexibility remains after accepting obligations and includes an integrated detection of conflicts in the planned schedule of a BESS. It is shown that the model is quickly computable and does not need much data volume during transmission.
Brandt, J.; Frost, E.; Ferenz, S.; Tiemann, P.H.; Bensmann, A.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R.; Nieße, A. (2022): Choosing the right model for unified flexibility modeling, Energy Informatics 5(1). Online verfügbar unter: DOI: 10.1186/s42162-022-00192-w
Using aggregated flexibility from distributed small-scale power devices is an extensively discussed approach to meet the challenges in modern and increasingly stochastic energy systems. It is crucial to be able to model and map the flexibility of the respective power devices in a unified form to increase the value of the cumulative flexibility from different small-scale power devices by aggregation. In order to identify the most suitable approach for unified flexibility modeling we present a framework to evaluate and compare the advantages and disadvantages of already existing modeling approaches in different levels of detail. As an introduction to flexibility modeling and as a basis for the evaluation process we initially provide a comprehensive overview of the broad range of flexibility models described in scientific literature. Subsequently, five selected modeling approaches allowing the generation of a unified flexibility representation for different power devices are presented in detail. By using an evaluation metric we assess the suitability of the selected approaches for unified flexibility modeling and their applicability. To allow a more detailed performance analysis, the best evaluated models are implemented and simulations with different small-scale devices are performed. The results shown in this paper highlight the heterogeneity of modeling concepts deriving from the various interpretations of flexibility in scientific literature. Due to the varying complexity of the modeling approaches, different flexibility potentials are identified, necessitating a combination of approaches to capture the entire spectrum of the flexibility of different small-scale power devices. Furthermore, it is demonstrated that a complex model does not necessarily lead to the discovery of higher flexibility potentials, and recommendations are given on how to choose an appropriate model.
Majumdar, N., Sarstedt, M., Hofmann, L. (2021): A Fast and Accurate determination of the Fea-sible Operating Region for Aggregation of Distribution Grid Potentials using Linearized Optimization, in Dresdener Kreis 2021.
Teimourzadeh Baboli, P., Brand, M., Lehnhoff, S. (2021): Stochastic Correlation Model-ling of Renewable Energy Sources for Provision of Ancillary Services using Multi-di-mensional Copula Functions, in 11th Smart Grid Conference (SGC2021), Tabriz, Iran, 2021.
Majumdar, N., Sarstedt, M., Leveringhaus, T., Hofmann, L. (2021): Linearized Optimization for Reactive Power Dispatch at Transmission Grid Level considering Discrete Transformer Tap-Settings, in 13th IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference 2021 (APPEEC) (S. 1-6).
Zare Oskouei, M., Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B., Teimourzadeh Baboli, P., Babazadeh, D. (2021): Ro-bust Stochastic Optimization for Energy Sharing between Multi-Carrier Microgrids us-ing Transactive Energy Management System, ETG Kongress, Wuppertal, Germany, 2021.
Wussow, J., Babazadeh, D., Beutel, V., Buchholz, S., Geissendörfer, S., Gerlach, J., Majumdar, N., Maydell, K., Narayan, A., Hoffmann, M., Kahl, L. (Paper), Leveringhaus, T., Lotz, M., Scheunert, A., Teimourzadeh Baboli, P., Tiemann, P., Huxoll, N., Wegkamp, C. (Vortrag), Werth, O., Agert, C., Breitner, M., Engel, B., Hofmann, L., Könemund, M., Kurrat, M., Lehnhoff, S., Nieße, A., Weyer, H. (2021): SiNED-Ancillary Services for Reliable Power Grids in Times of Progressive German Energiewende and Digital Transformation, ETG Kongress, digital, 18.-19. Mai 2021.
Within SiNED research project, several members of the Energy Research Centre of Lower Saxony (Energieforschungszentrum Niedersachsen, EFZN) are working on various issues relating to the future provision of ancillary services and to future congestion management. The questions include energy technology, economic and energy law aspects as well as information and communications technology (ICT) and data. The investigations are based on Lower Saxony and the framework conditions there. The temporal focus of the investigations is the year 2030.
Buchholz, S.; Tiemann, P.; Wolgast, T.; Scheunert, A.; Gerlach, J.; Majumdar, N.; Breitner, M.; Hofmann, L.; Nieße, A.; Weyer, H. (2021): A Sketch of Unwanted Gaming Strategies in Flexibility Provision for the Energy System in Energy Informatics and Electro Mobility ICT. Unter Mitarbeit von Michael H. Breitner, Sebastian Lehnhoff, Astrid Nieße, Philipp Staudt, Christof Weinhardt, Oliver Werth. 16th International Conference on Wirtschaftsinformatik, Pre-Conference Community Workshop. Duisburg-Essen, March 8, 2021. Online verfügbar unter: https://oops.uni-oldenburg.de/5084/1/proceedings_ow_sto_2021.pdf
Market-based procurement of system services is underway. Flexibility markets, however, are subject to a gaming risk. Different market participants can deteriorate the grid condition by their market behavior or physical actions, to generate flexibility demands and therefore potential profits, resulting in unreliable and unstable grid operation or economic inefficiencies. Such strategies are referred to as gaming. We investigate three gaming strategies regarding congestion management, reactive power management and balancing power provision. Further, we evaluate these strategies, and discuss solution techniques.
Tiemann, P.; Nieße, A. (2021): Assumptions on a Distributed and Hierarchical Market Concept for Balancing Reserve Aggregation in Energy Informatics and Electro Mobility ICT. Unter Mitarbeit von Michael H. Breitner, Sebastian Lehnhoff, Astrid Nieße, Philipp Staudt, Christof Weinhardt, Oliver Werth. 16th International Conference on Wirtschaftsinformatik, Pre-Conference Community Workshop. Duisburg-Essen, March 8, 2021. Online verfügbar unter: https://oops.uni-oldenburg.de/5084/1/proceedings_ow_sto_2021.pdf
While transmission systems have to be decoupleable in case of failures, up to now, there is no comparable procedure for controlled islanding of distribution grids. In this work, a concept for a balancing reserve market design is introduced, which would enable distribution grid operators to contract flexibility in order to operate their grids independently. Assumptions are presented on which such a market could be based and elements of it are presented. Furthermore, research gaps in order to develop such market are illustrated.
Gerlach, J.; Breitner, M. (2021): Smart Energy Systems: A Multidimensional Literature Review and Future Research Agenda in Energy Informatics and Electro Mobility ICT. Unter Mitarbeit von Michael H. Breitner, Sebastian Lehnhoff, Astrid Nieße, Philipp Staudt, Christof Weinhardt, Oliver Werth. 16th International Conference on Wirtschaftsinformatik, Pre-Conference Community Workshop. Duisburg-Essen, March 8, 2021. Online verfügbar unter: http://oops.uni-oldenburg.de/5084/1/proceedings_ow_sto_2021.pdf
Digital transformation, decentralization, and decarbonization of the energy sector are significant challenges for the next decades. Renewable energies and smart energy systems enabled by advanced information and communication technologies influence and transform, e.g., business models, customer behavior, governmental regulations, and technological innovations. However, there is still limited multidimensional research of future avenues for smart energy systems' digital transformation process. We conducted a systematic literature review facilitated by the PESTEL framework and a hierarchical clustering analysis to address this research need. We created a heat map to visualize research intensities in different areas, identified six critical topics in smart energy system research, and derived a future research agenda.
Scheunert, A.; Gerlach, J.; Weyer, H.; Breitner, M. (2021): Datenschutz und Privatsphäre in smarten Stromnetzen: eine interdisziplinäre Analyse und Trends in Energy Informatics and Electro Mobility ICT. Unter Mitarbeit von Michael H. Breitner, Sebastian Lehnhoff, Astrid Nieße, Philipp Staudt, Christof Weinhardt, Oliver Werth. 16th International Conference on Wirtschaftsinformatik, Pre-Conference Community Workshop. Duisburg-Essen, March 8, 2021. Online verfügbar unter: http://oops.uni-oldenburg.de/5084/1/proceedings_ow_sto_2021.pdf
Stark zunehmende Informationsflüsse in zukünftigen Stromnetzen stellen eine Herausforderung für Datenschutz und Privatsphäre dar. Wie diesen Herausforderungen begegnet werden kann, wurde mittels Interviews und einer umfangreichen Literaturanalyse ermittelt, wobei einerseits daraus resultierende Akzeptanzprobleme und andererseits die Ausgestaltung der rechtlichen Rahmenbedingungen fokussiert wurde. Zur Bewältigung dieser kritischen Herausforderungen dient die proaktive, allgemeinverständliche Aufklärung und Information von Betroffenen, aber auch der rechtliche Rahmen muss stetig weiterentwickelt werden.
Gerlach, J.; Eckhoff, S.; Werth, O.; Kraschewski, T.; Brauner, T.; and Breitner, M. (2021): Classification of Real-World Microgrids Based on a Morphological Analysis. AMCIS 2021 Proceedings. Online verfügbar unter: https://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2021/green_IS/sig_green/5/
Microgrids integrate distributed energy resources into an energy network reliably and efficiently. However, research of real-world examples at the international level is limited. We conduct a morphological analysis for microgrid design options to examine the status quo of academic literature. We identify 18 dimensions with 60 characteristics divided into the five layers governance, business, intelligence, communication, and physical. Subsequently, we classify 30 real-world microgrids with diverse types and locations using our morphological box. Our analysis reveals future research requirements regarding social aspects, business models, critical success factors, and maturity levels. We provide a framework supporting decision-makers to identify microgrid design options and promote socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable, resilient, and decentralized energy supply.
Lotz, M.; Majumdar, N.; Beutel, V.; Gerlach, J.; Wegkamp, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Kahl, L.; Wussow, J.; Schlachter, H.; Agert, C.; Breitner, M.; Engel, B.; Geißendörfer, S.; Hofmann, L; Könemund, M.; Kurrat, M.; Leveringhaus, T.; Maydell, K. (2021): Potentials and Technical Requirements for the Provision of Ancillary Services in Future Power Systems with Distributed Energy Resources. NEIS 2021 - Conference on Sustainable Energy Supply and Energy Storage Systems, digital, 13.-14. September 2021.
A decentralized supply of electrical power based on renewable energies paves the way to a sustainable power supply without nuclear energy and without the emission of greenhouse gases. This energy transition (Energiewende) entails challenges regarding the provision of Ancillary Services (AS), associated with intermittent in-feed of Distributed Energy Resources (DER) into the distribution grids. In this paper, the demand, potentials, and technical requirements for AS provision in Germany, especially in the state of Lower Saxony, are discussed. These aspects are considered from multiple perspectives across all voltage levels. Beginning with a steady-state analysis that focuses on the transmission grid, an expected increment in voltage violations and line congestions is revealed. Counteracting the resulting technical limit violations requires consideration of distribution grid flexibilities among others. To address this emerging demand, the potentials for the provision of AS by components in the distribution grids are identified. However, technical concepts are also required to exploit the potential, as DER in-feed has significant impact on the functionality of conventional protection systems. The analysis in this paper indicates the need for development of concepts to provide AS in the distribution grid and detailed technical requirements within a holistic simulative approach.
Tiemann, P. (2021): Balancing grid islands with distributed energy resources. In: Abstracts of the 10th DACH+ Conference on Energy Informatics. Energy Inform 4, 26.
Majumdar, N., Sarstedt, M., Leveringhaus, T., & Hofmann, L. (2021): Linearized Optimization for Reactive Power Dispatch at Transmission Grid Level considering Discrete Transformer Tap-Settings. In: 13th IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference 2021 (APPEEC) (S. 1-6).
Research indicates that an efficient operation of power systems, requires the use of optimization techniques for minimizing objectives such as grid losses, dispatch costs, reducing potential technical constraint violations etc. These are referred to as optimal power flow (OPF) techniques. Over the years different optimization techniques have been developed based on analytical methods, heuristics and stochastic based approaches. Analytical methods include for example linear and quadratic optimization approaches. Metaheuristic methods like Particle Swarm optimization (PSO) and Genetic Algorithms (GA) have also been developed and researched upon. In this paper, a successive mixed integer linear optimization programming (sMILP) based method in the context of optimal reactive power flow (ORPF) is developed considering continuous reactive power flexibilities and discrete transformer tap-sets. The novel formulation of the transformer tap sensitivities indicate its efficiency of using discrete tap-settings and ease of implementation in the context of Linear Programming. This method is further compared to an already established PSO-based method subject to similar initial grid conditions and three different voltage constraint violation case studies. Results indicate the reliability and efficiency of the method.
Majumdar, N., Sarstedt, M. Hofmann, L. (2021): A Fast and Accurate determination of the Feasible Operating Region for Aggregation of Distribution Grid Potentials using Linearized Optimization. In: Dresdener Kreis 2021.
Increased renewable penetration over the years result in the decommissioning of thermal power plants, that reliably contribute to ancillary service provision. In order to alleviate this deficiency, an increasing number of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) are required to provide ancillary system services. The major share of the DERs are being installed at the Distribution Grid level. Therefore, Medium and Low voltage grid level that previously passively consumed electricity are transitioning towards a more active role. Active Distribution Grid support services to support the transmission level operation include frequency control, voltage control, congestion management among others. In order to evaluate the Distribution Grid potentials for ancillary service provision, an aggregation of potentials can serve as a bridge between the Transmission System Operators (TSO) and Distribution System Operators (DSO). Therefore, the Feasible Operating Region (FOR) is an aggregation of the Distribution Grid active and reactive power flexibility (P- Q flexibility) potentials. The FOR can be used by the network operators during planning of system support services. Over the years, different approaches for evaluating the FOR have been determined considering mathematical optimization, stochastics and metaheuristic programming approaches. In this paper, strategies for a fast and accurate determination of the FOR using a Linearized Optimization are discussed. Results reveal the efficiency of the methods to counteract the over/under-estimation of the objective with linearized sensitivities.
Lotz, M. R., Kurrat, M. (2021): Evaluation of Temporary Overvoltages Considering Current Standards and Regulations with Extensive Renewables Integration. ETG Congress 2021, S. 1-6.
The extensive integration of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) and electromobility requires a review of the protection systems in Low Voltage (LV) networks and customer installations. This paper provides an evaluation of Temporary Overvoltages (TOVs) in LV AC grids regarding current standards and regulations, when there is such an extensive integration. This could lead to asymmetric load configurations, causing TOVs when a Loss of Neutral (LoN) occurs. The results show that current regulations, mainly the Niederspannungsanschlussverordnung, permit the operation of highly asymmetric load configurations.Within the permitted range, the expected TOVs are lesser than explicit test and withstand voltages of facilities and devices, so that no further consideration is planned.